The ketogenic diet has gained popularity over the years thanks to its health benefits of promoting weight loss, lowering blood pressure, and enhancing brain and cognitive function.
When we talk keto diet, our main focus is on its effects on insulin resistance. The ketogenic diet’s benefit of improving insulin resistance is what has attracted attention to eating a keto diet as a preventive treatment for chronic and other diseases.
Today, we will focus on keto PCOS to answer the questions in many people’s minds: which is the best diet to manage PCOS symptoms? Is keto good for PCOS? What is the mechanism of action of restricting carbohydrates associated with managing PCOS symptoms?
Is Keto Good for PCOS?
The keto diet has basic rules: low carbohydrate intake, high fat, and moderate protein consumption. Carb intake increases inflammation and contributes to hormonal imbalances. Your eating of high-carbohydrate foods may be contributing to polycystic ovary syndrome.
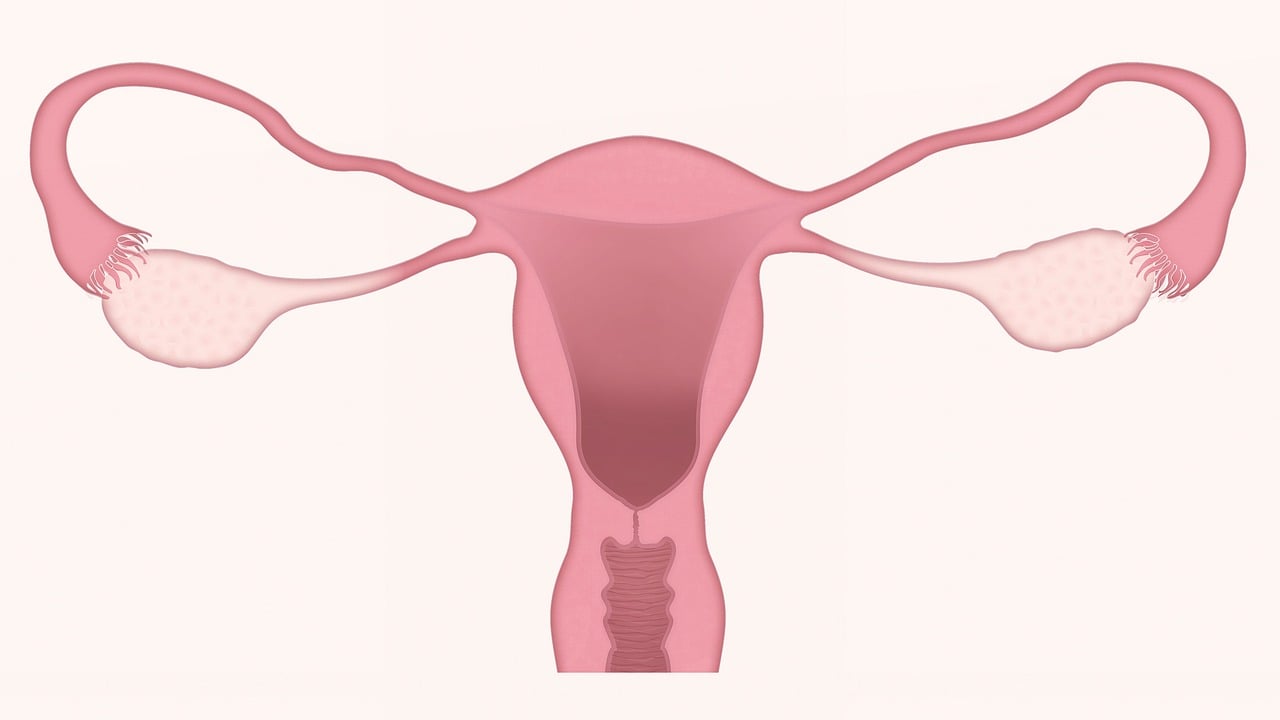
Polycystic ovarian syndrome, popularly known as PCOS is an endocrine disorder that affects women of childbearing age, especially overweight and obese women, altering the functions of the ovary and ovulation. According to the U.S Department of Health and Human Services, Office on Women’s Health (OHW) one in 10 women of childbearing age suffer from polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
The underlying causes of this hormonal disorder are yet to be known but several factors can contribute to its development. These include inflammation and hormone imbalance of insulin and the male hormones or androgens. Increased insulin levels increase the production of androgens in the body. Overweight women and obese women are at a higher risk of insulin resistance, further worsening PCOS symptoms.
Women normally produce and use a little testosterone, but in women with PCOS, there is an overproduction and high testosterone levels.
Low-carb diets and high fat intake control glucose levels and improve insulin resistance by improving lipid and glucose metabolism. Restricting carbs can reduce inflammation through nutritional ketosis.
Low Carb Vs Keto for PCOS
Restricting carbs can be good for polycystic ovary syndrome, but it can cause problems if the restrictions are too intense. If you restrict carbohydrates too much below the recommended intake, you may stress your body making the adrenal gland produce more cortisol stress hormone. This could worsen the symptoms of PCOS. The keto diet restricts but does not eliminate carb intake.
When using keto to manage PCOS, go for the less restrictive types of the ketogenic diet. A very low-calorie ketogenic diet may be a better choice than a very low-carb diet.
Other low-carbohydrate diets like paleo may restrict eating carbohydrate foods but allow for the consumption of high-starch foods from other food groups.
Fruits may not be carbs, but they are high in sugar which could spike insulin levels and worsen insulin resistance. Paleo is not good for PCOS because it allows for the consumption of high-carb and high-glycemic-index foods that increase insulin resistance.
Keto Diet for PCOS
The keto diet for PCOS is an effective low-carb diet for treating PCOS. This is because it removes the root cause of polycystic ovary syndrome, carbs, that cause inflammations in the body. Let’s look at how a keto diet affects contributing factors of PCOS to increase insulin sensitivity and restore normal hormonal function.
Is Keto Good for Insulin Resistance With PCOS?
Insulin is involved in the regulation of blood sugar in the body by increasing the absorption of glucose by the cells. When you have insulin resistance, your body’s response to the elevated blood sugar levels due to reduced cell sensitivity is to produce more insulin increasing blood insulin levels.
A keto diet restricts carb intake, which lowers blood glucose levels in the body. When there’s inadequate glucose, glycogen, and proteins are converted to glucose to fuel the body. Once these are depleted the body is forced to use its secondary fuel source, fat, as fuel. This switch from glucose metabolism to fat metabolism is what improves insulin resistance.
Is keto good for PCOS? Yes, because it increases cell insulin sensitivity by switching the body’s fuel from glucose to ketones. Ketosis triggers weight loss which also further improves insulin sensitivity and reduces insulin resistance.
Keto PCOS Weight Loss
As mentioned, nutrition ketosis is triggered when glycogen stores are depleted and no more glucose can be made through gluconeogenesis. Reduced insulin levels lead to fat oxidation from adipose tissue, glucagon-induced lipolysis, and the production of ketones to be used as metabolic fuel.
What you need to know is nutrition ketosis reduces the need for endogenous glucose and provides the body with fuel for metabolic function. It also spares the use of amino acids from lean muscle mass and instead uses fat mass in storage as a fuel source which helps you to lose weight.
Further consuming a high-fat diet is to burn fat even as your body is in ketosis. Eating a low-carb diet will trigger ketosis but pumping your body with healthy fats will provide more fuel in the form of dietary lipids to maintain ketosis. This is what prevents further weight gain and helps you to continuously lose weight.
Keto Diet For Menstruation and Pregnancy In PCOS
Reduced insulin levels lower androgen levels in the body. Moreover, weight loss improves fertility. The Keto diet for PCOS improves insulin resistance and promotes weight loss helping to restore normal hormonal balance, ovulation, and menstrual cycle and increasing pregnancy rates.
Lower insulin levels decrease androgen secretion and increase circulation of sex hormone binding globulin (SHB) which limits the circulation of androgens in the blood. Moreover, the keto diet reduces the luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) ratio resulting in the balance of endocrine parameters.
Keto and PCOS Study
Several studies have provided evidence of the effectiveness of the ketogenic diet in managing the contributing factors of PCOS. These studies show improvements in patients’ body composition and biochemical tests.
Insulin Regulation
A study on subjects with obesity and PCOS to assess the effects of a ketogenic Mediterranean diet showed improvements in patients in terms of blood glucose and insulin regulations and significant improvements in insulin resistance.
Another study on subjects with obesity and PCOS to investigate the effects of a mixed keto diet reported a reduction in insulin concentration attributed to the depletion of muscle and liver glycogen stores and a reduction in glycemia.
Weight Management
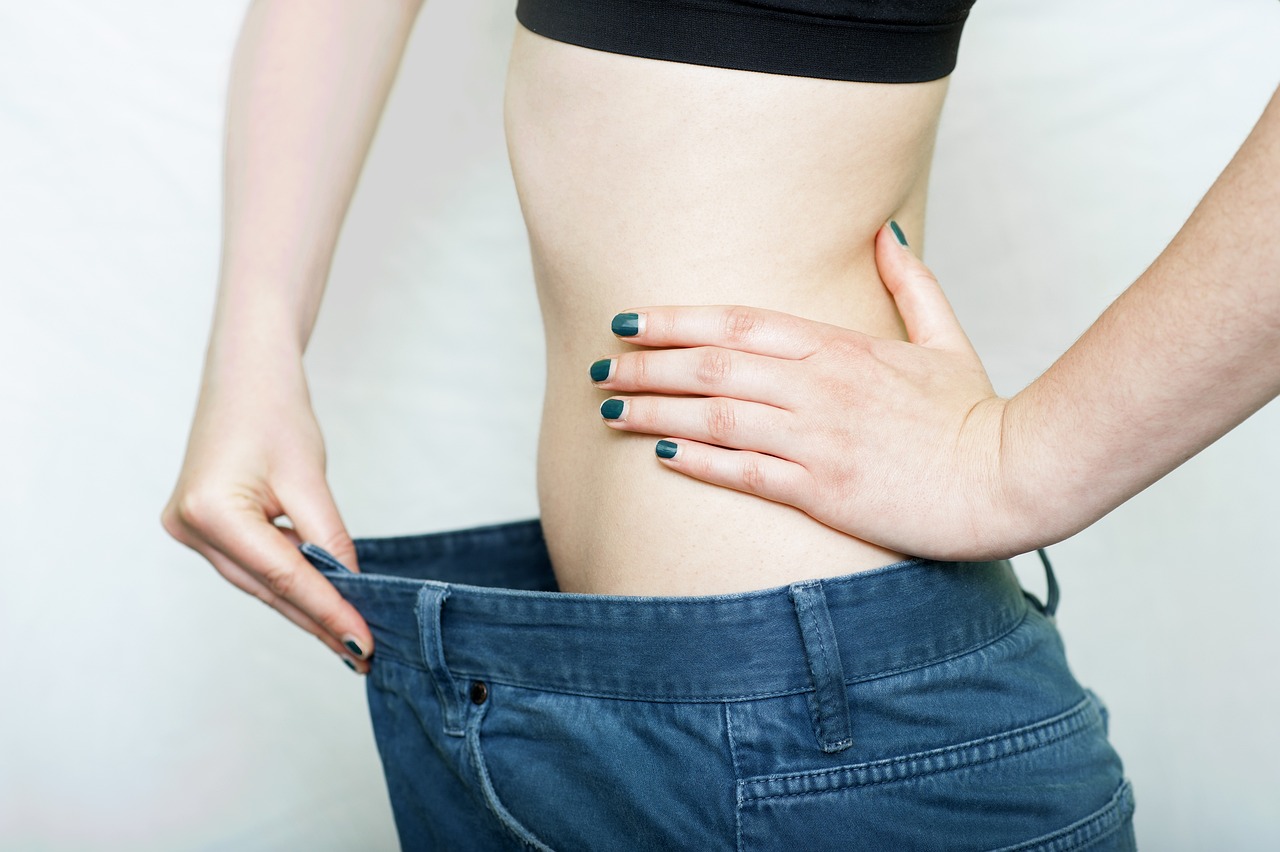

The subjects with obesity mentioned in this study experienced a significant reduction in body weight, losing weight of about 20 pounds in 12 weeks. There was also an improvements in patients body mass index (BMI).
In another study, 17 subjects with obesity and PCOS consuming 10g to 20g of carbs per day experienced a reduction in body weight and body mass index (BMI). Ketosis improves body weight and body composition by reducing fat mass.
Studies have confirmed that the keto diet is as effective as a low-fat diet for rapid weight loss and maintaining a healthy weight.
Improves Lipid Profile in Women with PCOS
A study on women with PCOS and liver dysfunction who were obese was done to assess the effects of a keto diet on liver function. Consumption of a keto diet reduced liver function markers. There was a drop in total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol and an increase in HDL cholesterol, proving a significant improvement in lipid profile in women with PCOS.
The 14 women also experienced an improvement in lipid profile. Their total cholesterol, bad cholesterol, and triglyceride levels dropped while the good cholesterol increased. A good lipid profile reduces one’s risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular issues.
It is safe to say that eating keto improves endocrine parameters. To answer your question again is keto good for PCOS, yes it is, since it helps reduce cardiovascular risk factors and improves metabolic health.
Keto Diet, PCOS Fertility
In this study, two women got pregnant despite previous infertility problems, 5 women had their period return after several years and 12 women reported that the regularity of their flow had improved.
There was also an improvement in symptoms of PCOS like skin tags and acne and thinning hair due to the restoration of normal hormonal levels.
Metformin and Keto Diet for PCOS
One way to treat polycystic ovary syndrome is using diabetes mellitus medication. Your healthcare provider can prescribe Metformin diabetes medication to help lower insulin resistance in polycystic ovary syndrome. It can help reduce circulating insulin levels and lower androgen levels in the body, assisting with symptoms of PCOS management.
The ketogenic diet has been proven to be an effective nutritional management method for increasing insulin sensitivity. Using both Metformin and the keto diet can help reduce insulin resistance and improvements in patients with PCOS suffering from infertility.
It is safe to restrict carbs while on Metformin. Physiological ketosis promotes fat burn which reduces insulin levels in the body, which further assists in the management of insulin resistance.
Why is Keto Bad for PCOS?
We have discussed reasons why a low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet can be a good choice for women suffering from Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome, however, there are cons to using this diet in the management of this condition.
This Can Lead to Nutrient Deficiencies
Being on a low-carb diet, especially the ketogenic diet puts you at risk of nutrient deficiencies like potassium and magnesium deficiency. Many nutritionists advise multivitamins and mineral supplementation while on keto.
Women with obesity and PCOS using birth control as a pharmacological therapy face a greater risk of micronutrient deficiencies while on keto than those on other treatment methods. Carb restriction can worsen your PCOS if you are on birth control.
Can Trigger Disordered Eating
The keto diet can be great for achieving long-term weight loss. However, it can be mentally tasking for obese patients with metabolic disorders and infertility issues. Women with PCOS are at a higher risk of developing an eating disorder compared to the general population.
Limiting your calorie consumption and carbohydrates per day can have someone obsessing about how much they eat. For these patients do not overemphasize a hypocaloric diet or seriously restricting carbohydrate consumption. Start with other methods of burning fat for fuel like aerobic exercise then build to nutritional management.
Maybe More Difficult to Adhere to for Women with PCOS
Sex-hormone imbalances or a general lack of hormone homeostasis is a PCOS Diet challenge. When suffering from PCOS you may face increased appetite, poor body image, and lack of control, all of which can lead to binge eating.
Since overconsumption of foods rich in carbohydrates can kick you out of physiological ketosis, this nutritional management method may be ineffective.
May Not Be A Feasible Long-term Plan
The studies that are for the keto diet for PCOS management are short-term. Other studies done for longer than six months show some adverse effects of using physiological ketosis for PCOS.
One study showed that 45% of the adolescents on the ketogenic diet experienced menstrual dysfunction which is an adverse side effect of ketosis.
Another study investigating the effects of varying carbohydrate restriction on thyroid hormone showed that a very low-calorie diet and a low-carbohydrate diet had positive effects on body composition in women. However, the low-GI diet had a negative effect on thyroid function. Individuals with thyroid dysfunctions have been shown to have lower Vitamin D levels. Lower vitamin D levels translate to poor calcium homeostasis.
Polycystic ovarian syndrome already increases your risks of thyroid dysfunction, bringing keto into the picture will worsen your situation.
Is Fasting Good for PCOS
Intermittent fasting creates a calorie deficit triggering the body to enter a fasting state. Weight loss on IF may be difficult because of the large intake of high-carb meals during the eating window.
But, intermittent fasting while on a keto diet introduces autophagy into the picture. Autophagy is the body’s cleaning system. Your body breaks down damaged proteins and uses these components to make new healthier proteins. This prevents the breakdown of lean mass in the body.
You can consider fast keto or speed keto dieting if you want to introduce intermittent fasting to your keto diet. Speak to your healthcare provider before you start fasting to get the go-ahead to do so.
What are the Biggest Signs of PCOS?
The main symptoms of PCOS are:
- Abnormally high levels of male hormones
- Menstrual irregularities or lack of menstrual cycle
- Development of ovarian cysts
Other symptoms of PCOS are weight gain or obesity, metabolic diseases, excess hair growth, skin changes like skin tags and acne, and male-pattern baldness or thinning hair.
The following put you at risk of developing PCOS:
- Inflammation in women
- Insulin resistance
- Metabolic syndrome
- Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Genetics
- Overweight and obesity
- Increased androgen levels
- Poor dietary habits
- Previous infertility problems
- Sedentary lifestyle
How Do I Know What Type of PCOS I Have?
The presence of symptoms of PCOS doesn’t necessarily mean you have PCOS. On the other hand, not every woman with PCOS has irregular periods or unwanted hair growth.
Most of these symptoms can be brought about by other health conditions. If you are a woman of reproductive age, and you have elevated levels of insulin or insulin resistance or a combination of all these symptoms, you should visit a gynecologist or reproductive endocrinologist.
PCOS is a syndrome that cannot be diagnosed by a single test. The Rotterdam Diagnostic Criteria is used to diagnose PCOS. For it to be said that you are suffering from PCOS, you have to meet two out of three of the following diagnostic criteria:
- Hyperandrogenism: through clinical diagnosis by the presence of acne or male-pattern baldness or through blood tests to check testosterone levels
- Ovulatory dysfunction: through clinical diagnosis by oligomenorrhea characterized by menstrual cycles more than 35 days, but less than 6 months apart. It can also be diagnosed by amenorrhea which is the absence of menstruation for 6 to 12 months.
- Polycystic ovaries: diagnosed through an ultrasound.
Blood tests are used to diagnose PCOS. A Glucose Tolerance Test can measure your body’s response to glucose. Glucose intolerance is a sign of PCOS.
Key Takeaway
Although the exact cause of PCOS is unknown, inflammation and insulin are contributing factors to this syndrome. Restricting carbs reduces these factors.
So, is keto good for PCOS? Yes, the ketogenic diet is good for the job of PCOS management. However, before starting your diet, speak to your healthcare provider to know how to deal with the cons that come with keto for PCOS.
Tell me in the comment section if you or anyone you know has used the keto diet for PCOS management. Has it improved your situation? Share your experience in the comment section.