Since time immemorial the importance of eating fruits has been shouted from the high heavens. Fruits contain vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber necessary for the proper function of the body. Nutritionists and dietitians have made it clear that fruits are part of a healthy diet.
People with weight loss goals or those with metabolic syndrome have had to modify their diet to suit their nutritional needs. The low-carb, high-fat keto diet is one of those dietary modifications. But the consumption of fruits is still as important when you carb count.
Fruits have a high carb count because they contain more sugars than vegetables. Does that mean we should completely ban fruits from our keto diet because they are high in carbs? No. Some fruits have a lower glycemic index and glycemic load because they are high in fiber and have less amount of sugar. Others are high in fat, making them a good choice for the keto diet.
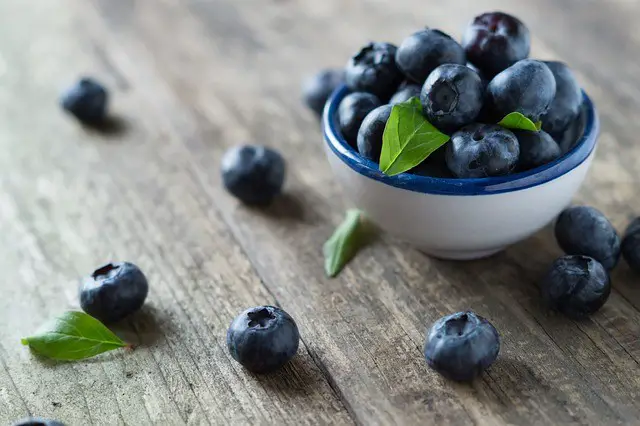
Avocados and berries are low-carb fruits considered keto foods. Berries like blackberries, blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are allowed on a keto diet. Blueberry fruit is packed with nutrients that can benefit your health. Allow me to answer for you the most important questions on blueberries. How many carbs in 1 cup of blueberries? What health benefits will you enjoy if you consume blueberries every day? How can you incorporate blueberries into your keto diet? What are the carb counts of other berries?
How Many Carbs in 1 Cup of Blueberries?

Fresh blueberries are quite a versatile fruit! You can snack on them, add them to your salad, enrich your smoothies with them, and even sweeten your Greek yogurt by adding raw blueberries to it. Why are they good for the low-carb, high-fat keto diet?
Blueberries Nutrition facts
These are the nutrition facts of one cup of raw blueberries according to the USDA:
- Energy: 84 calories
- Protein: 1 g
- Fat: 0.5 g
- Total carbs: 21 g
- Sugars: 15 g
- Fiber: 3.6 g
- Net carbs: 17.4 g
- Sodium: 1.5 mg
- Vitamin C: 14.4 mg
- Vitamin K: 28.6 mcg
- Vitamin E: 0.8 mg
- Vitamin B6: 0.1 mg
How many carbs in a half a cup of blueberries?
One half a cup of dried blueberries contains:
- Energy: 190 calories
- Protein: 1 g
- Total Carbs: 48 g
- Fiber: 5 g
- Net Carbs: 43 g

Unsweetened dried blueberries contain fewer carbs than sweetened dried blueberries because sugar increases carb count. According to this nutrition information, blueberries are high in carbohydrates. But how come despite the high sugar content of these delicious berries, they are still acceptable on a low-carb diet?
Are Blueberries Keto-Friendly?

Blueberries may contain more carbs in one cup than other berries but are considered keto-friendly. The glycemic index (GI), which is the measure of how quickly foods increase blood sugar, of raw blueberries is 53, which is considered a low GI. The glycemic load, which represents how much foods raise blood sugar levels, is 4. What this means is, if you eat blueberries, they will raise blood sugar levels at a much slower rate, making them a great delicious choice for type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
I would recommend squeezing in a quarter or one-half a cup of blueberries into your diet when meal planning. Pay close attention to the portion sizes of this fruit, because the more you eat the more net carbs you add to your carb intake.
On keto, fresh blueberries are recommended over dried blueberries since they have fewer carbs. In addition, some dried blueberries contain added sugar, which adds to your total carbs.
Most processed foods have a high sugar content hence not recommended on a low-carb diet. As much as I am advocating for fresh blueberry fruit, my advice is to avoid store-bought blueberry jams and jellies, canned blueberry fillings, and blueberry fillings. These are high in sugar and calories, which could kick you out of ketosis.
What Are the Health Benefits of Blueberries?
We now know how many carbs in 1 cup of blueberries are, the total carbs, net carbs, and fiber content which is all important information for carb-conscious individuals. But why should you consume raw blueberries?
Nutrient Dense
In a serving of fresh blueberries, you will get almost 25% of the daily recommended value of vitamin C. Vitamin C is necessary for wound healing, and collagen formation and to give your immunity a boost.
In the same serving, you will get 36% of the daily value for vitamin K which promotes heart and kidney health, improves bone density, and is important for blood clotting. Moreover, one serving of blueberries contains 25% of the manganese recommended daily value. Manganese promotes bone health and helps in the metabolism of foods like carbs.
They are also rich in other micronutrients like calcium, zinc, phosphorous, and magnesium that make them a nutritious addition to your diet.
Improve Brain Function

Eating blueberries has been proven to improve mood and memory, and lower rates of cognitive decline. One small study to investigate neural activation with blueberry supplementation in mild cognitive impairment (MCI) showed an enhances neuronal response in blueberry-supplemented older adults with cognitive decline.
Another randomized trial found that eating blueberries had a positive effect on mood and cognitive performance.
This improvement is attributed to its antioxidative properties, whose action in our hippocampus, the part of the brain that controls memory, reduces stress-related changes that can reduce the functioning of our brain cells as we age.
Rich in Antioxidants
One of the nutrients the blueberry fruit can boast of is antioxidants. An antioxidant reduces cell damage from reactive oxygen species. Blueberries are rich in phytochemicals that reduce oxidative stress in the body and promote gastrointestinal health.
An important antioxidant in blueberries, anthocyanins have gained much interest in improving health and functionality Eating blueberries rich in anthocyanins has been associated with lower risks of heart disease and diabetes and disease-related mortality, neuroprotection, blood sugar regulation, and weight maintenance. Did you know, it is anthocyanins that give blueberries their blue hue? Now you know!
Blood Pressure Lowering Benefits
A randomized controlled trial on the effects of consuming blueberries on hypertension reported that daily consumption of blueberries lowers blood pressure and reduces arterial stiffness. This is attributed to the polyphenols in blueberries that increase the production of nitric oxide and reduces angiotensin II-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in endothelial cells of blood vessels.
People with hypertension should eat blueberries to lower blood pressure and alleviate biomarkers of cardiovascular disease.
Reduce Risks of Chronic Disease
Blueberries are rich in flavonoids that have been proven to reduce the risk of developing and the severity of certain cancers. Phytochemicals like flavonoids, anthocyanins, flavonols, and proanthocyanidins reduce the risks of vascular diseases like ischemic stroke, atherosclerosis, and neurodegenerative diseases.
Blueberry fruit components lower inflammation and damage by oxidative stress and regulate gene expression associated with disease pathophysiology.
Lowers Insulin Resistance
Insulin helps regulate blood sugar levels in the body. Blueberries are low in calories and have a low GI and glycemic load so do not easily spike blood sugar. Although blueberries contain carbohydrates, the phytochemicals in them increase insulin sensitivity. Consumption of raw blueberries can improve insulin resistance and lower the risks of diabetes.
Varieties of Blueberries

You can eat North American blueberries. There are cultivated or wild berry fruit options to pick from. Wild berries contain more phytochemicals and a richer flavor.
Fresh blueberries are in season from March to September, but that doesn’t mean you can’t enjoy them all year round. Frozen blueberries are a variety of blueberries you can enjoy at any time. You can use them as toppings, as an additional flavor for low-carb baked goods, in smoothies, and add Greek yogurt and cottage cheese.
Frozen berries are picked when peak ripe and have a longer shelf life compared to fresh ones. Freeze your berries at home, that way you will not add sugar which won’t affect carbohydrate content.
Are Other Berries Low Carb?

Now that we know how many carbs in 1 cup of blueberries, let’s find out if other berries are low in carbohydrates. These values represent carb count in 100 g.
- Strawberries: 7.96 g of total carbs, 2 g of fiber, and 5.96 g of net carbs. Strawberries have a glycemic index of 40 and a glycemic load of 3.
- Raspberries: 11.9 g of total carbs, 6.5 g of fiber, and 5.4 g of net carbs. The GI is 33 and the GL is 3.
- Blackberries: Blackberries contain 9.61 g of total carbs, 5.3 g of fiber, and 4.21 g of net carbs. Their GI is 25 and their GL is 2.02. This fruit is the best pick for keto compared to other berries.
How to Incorporate Blueberries into Your Low-Carb Diet

You can add blueberries to your baked goods at home. Use low-carb flour and sweeteners like monk fruit to lower carb intake. You can make a blueberry cobbler using almond flour, monk fruit sweetener, frozen blueberries, butter, and lemon juice. If you’re vegan, use coconut oil as a butter alternative.
Another option is blending blueberries into your smoothies. Because they have a sweet flavor you won’t need to add sugar to your drink. You can also top your smoothie bowl or Greek yogurt with blueberries.
The easiest and less complicated option, pick a one-half cup of berries and eat them as a snack. Don’t exceed a cup though, because you don’t want to exceed your carb limit, yet you will get carbs from other foods throughout the day.
Drug-Nutrient Interaction
If you are on some medications, you need to speak to your doctor before consuming blueberries. Polyphenols in blueberries can interact with blood thinner medications reducing their absorption in the body.
Bottom Line
Blueberries are low in net carbs making them keto-friendly. You can enjoy fresh blueberries or frozen ones all year round reaping their numerous health benefits. Pick fresh blueberries over dried ones because they have a lower carb content. Incorporate other berries like blackberries, raspberries, and strawberries into your diet for variety. Finally, speak to your dietitian to explain the interaction between polyphenols and blood thinners.
Which berry is your favorite? Drop your most delicious blueberries recipe in the comment section so your keto fam can see how you incorporate them into your diet. Enjoy your berries, with caution on portions!